Understanding Ground Heave
Ground heave is the upward movement of the ground surface caused by the expansion of clay soils when they absorb water. This phenomenon can cause significant damage to structures and infrastructure if not properly managed. Unlike subsidence, which involves the downward movement of the ground, ground heave poses unique risks to structural integrity, making it essential to address in construction projects.
The Impact Of Ground Heave
Ground heave can lead to:
- Foundation Cracks: The upward pressure can cause cracks in foundations, compromising the stability of buildings.
- Distorted Floors and Walls: Uneven ground movement can result in warped floors and walls, affecting the overall aesthetics and functionality of structures.
- Damage to Utilities: Underground utilities such as pipes and cables can be displaced or damaged, leading to costly repairs and service disruptions.
Traditional Solutions and Their Drawbacks
Historically, polystyrene cellular structures have been used to mitigate ground heave. These conventional solutions involve placing polystyrene void formers beneath foundations to create a void for ground movement. However, this approach has several drawbacks:
- Excessive Digging: Requires more excavation, increasing labour costs and project delays.
- Bulky and Cumbersome: Difficult to transport, handle, and store, leading to higher costs and logistical challenges.
- Fragility and Waste: Prone to damage, resulting in approximately 10% wastage and costly disposal.
- Environmental Concerns: Polystyrene is not environmentally friendly due to its molecular breakdown and static nature.
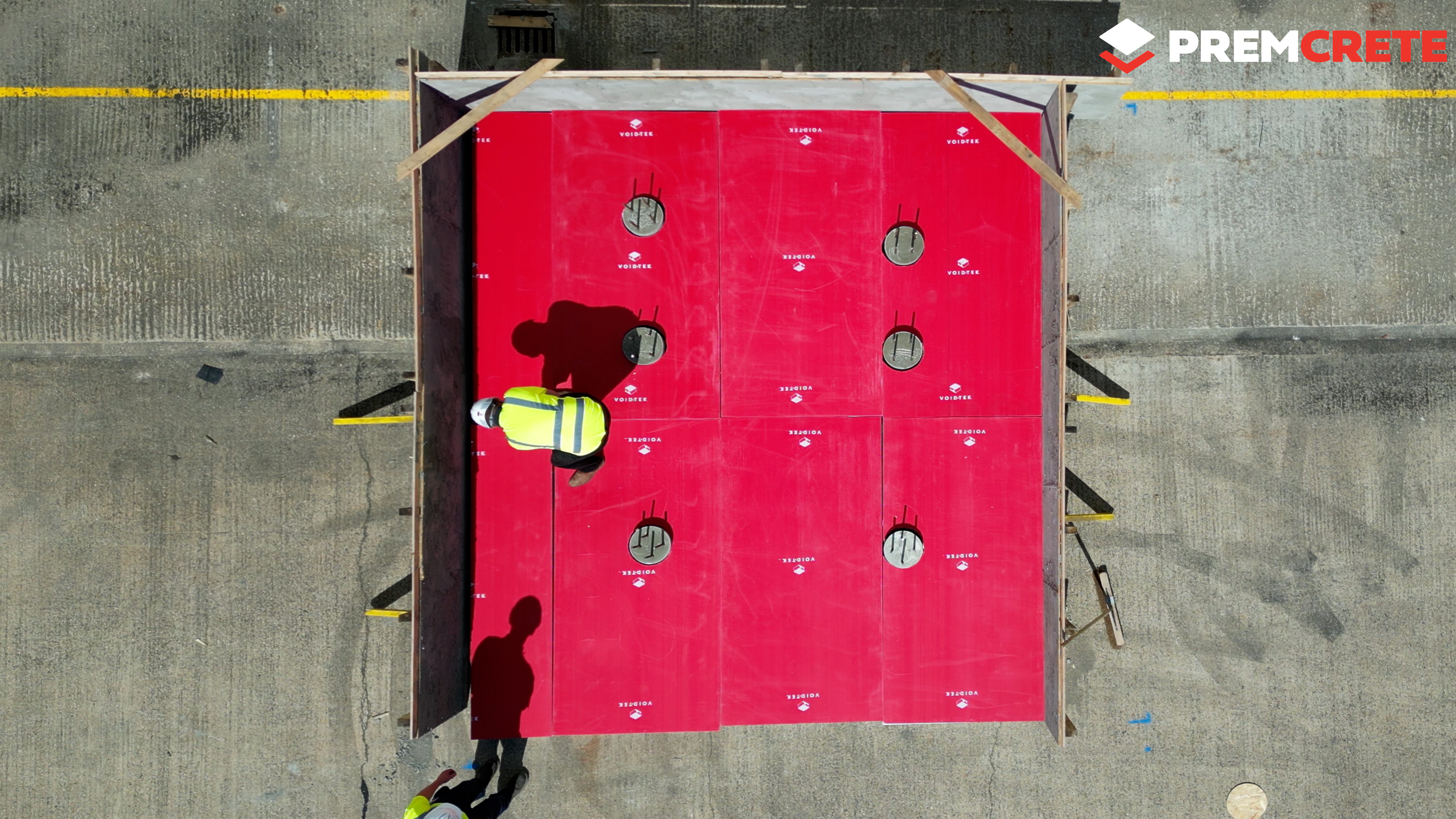
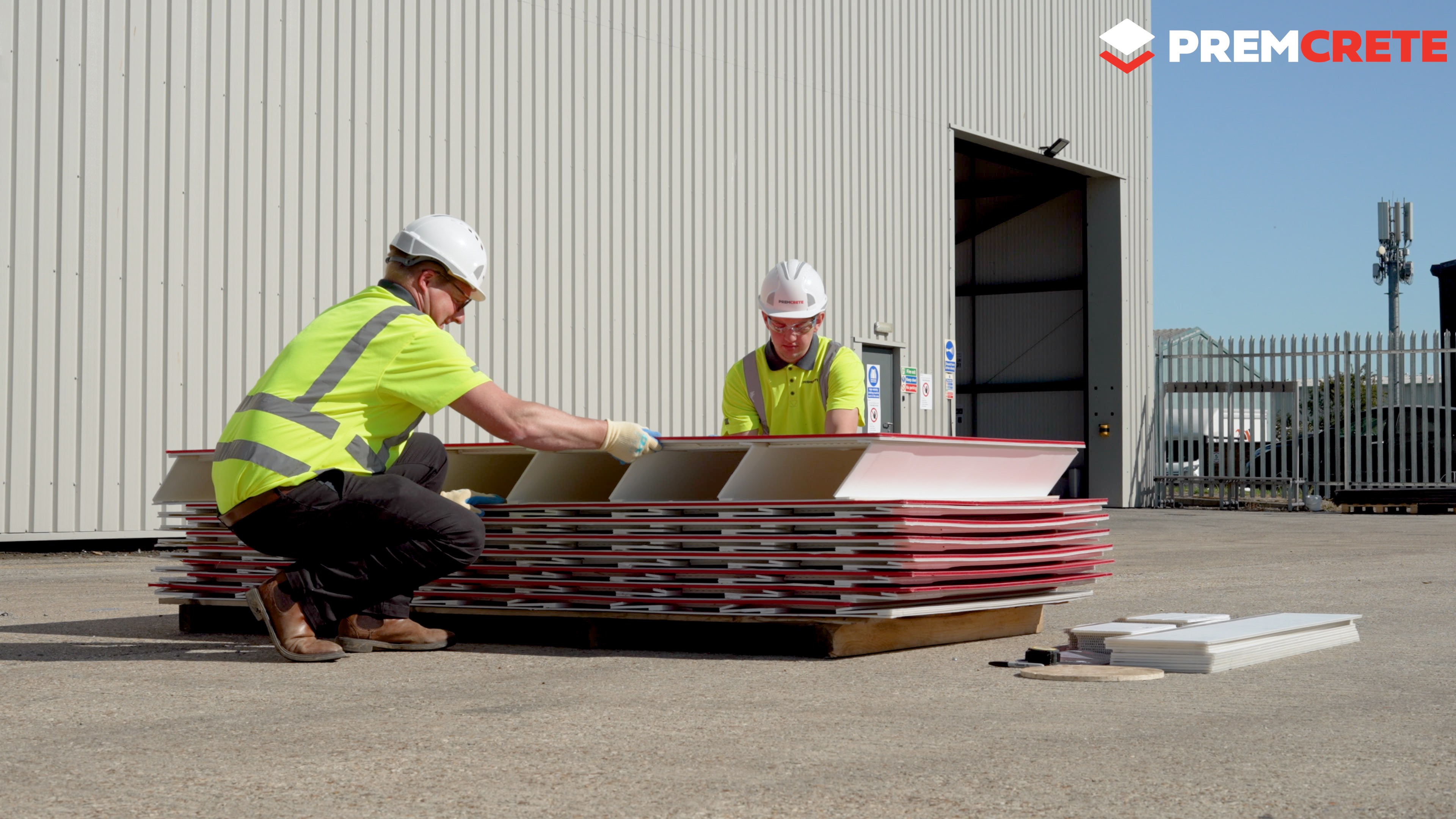
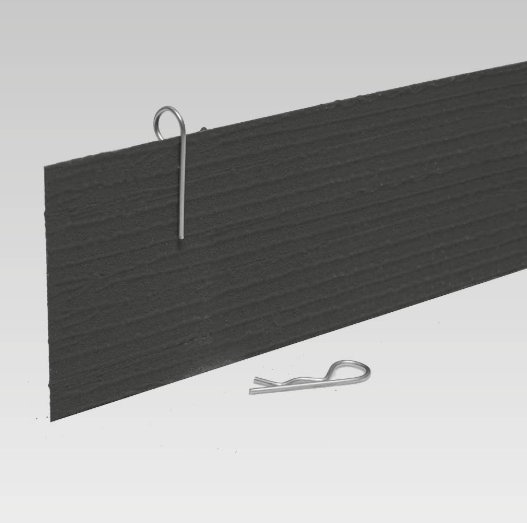
Introducing VOID-TEK by Premcrete
VOID-TEK is an innovative solution designed to overcome the limitations of traditional methods. Made from polypropylene fluted board, VOID-TEK offers high strength and durability. Here are some of its key benefits:
- Flat-Packed Delivery: Reduces transport costs and storage space requirements.
- Easy Installation: Quick to assemble, less breakage, and easy to cut with no mess.
- Environmental Benefits: Polystyrene-free, eliminating flaking and reducing environmental impact.

Advantages of VOID-TEK
- Reduced Digging: Saves labour and muck away costs.
- Strength and Flexibility: Rigid construction minimizes damage and wastage.
- Customizable: Can be ordered and configured to specific size requirements for various applications.
- Cost Savings: Lower transport, storage, and installation costs, along with reduced wastage and disposal expenses.

How to Specify Heave Protection Boards: A Guide to Using VOID-TEK
When building on clay soils, specifying the right heave protection solution is crucial to safeguard your structures from the effects of ground heave. Here’s a detailed guide on how to specify VOID-TEK heave protection boards, integrating both the information from the Void-Tek Specification Sheet and additional expert advice.
Step 1: Conduct A Soil Analysis
The first step in specifying a heave protection system is to analyse the soil for its plasticity index, which indicates the potential for clay to expand. Soil plasticity or Clay Plasticity is generally categorized into three bands:
- Low Plasticity: 10-20%
- Medium Plasticity: 20-40%
- High Plasticity: 40-60%
These values determine the potential ground movement and dictate the corresponding heave protection requirements.

Step 2: Determine The Required Void Depth
Based on the plasticity index identified, you can determine the required void depth as per the guidelines from NHBC or other building warranty providers. For instance:
- Low Plasticity (10-20%): Requires a void depth of around 50mm.
- Medium Plasticity (20-40%): Necessitates a void depth of 100mm.
- High Plasticity (40-60%): Demands a significant void depth of 150mm.
Step 3: Select the Appropriate VOID-TEK Product
Once the void depth requirement is understood, select the suitable VOID-TEK product code:
- VT50: For low plasticity soils.
- VT100: For medium plasticity soils.
- VT150: For high plasticity soils.
TABLE 1

Step 4: Choose The Right Grade Of Heave Protection
The grades of VOID-TEK correspond to the safe load and fail load capacities, which are crucial for ensuring the integrity of the foundation against ground heave pressures. Each grade supports a maximum concrete depth, which must be considered based on the structural design.
Safe loads represent the maximum weight and pressure that the heave protection board can handle from the concrete or foundation elements above it, while fail loads indicate the maximum pressure the board can withstand before failing under the forces exerted by ground heave.
Example: Grade 14/18 Supports a safe load of 14 kN/m², a fail load of 18 kN/m², and accommodates up to 500mm of concrete. If the clay plasticity was 40-60%, the required VOID-TEK code would be VT150 , and full the product code for this grade would be ‘VT150 14/18’
TABLE 2
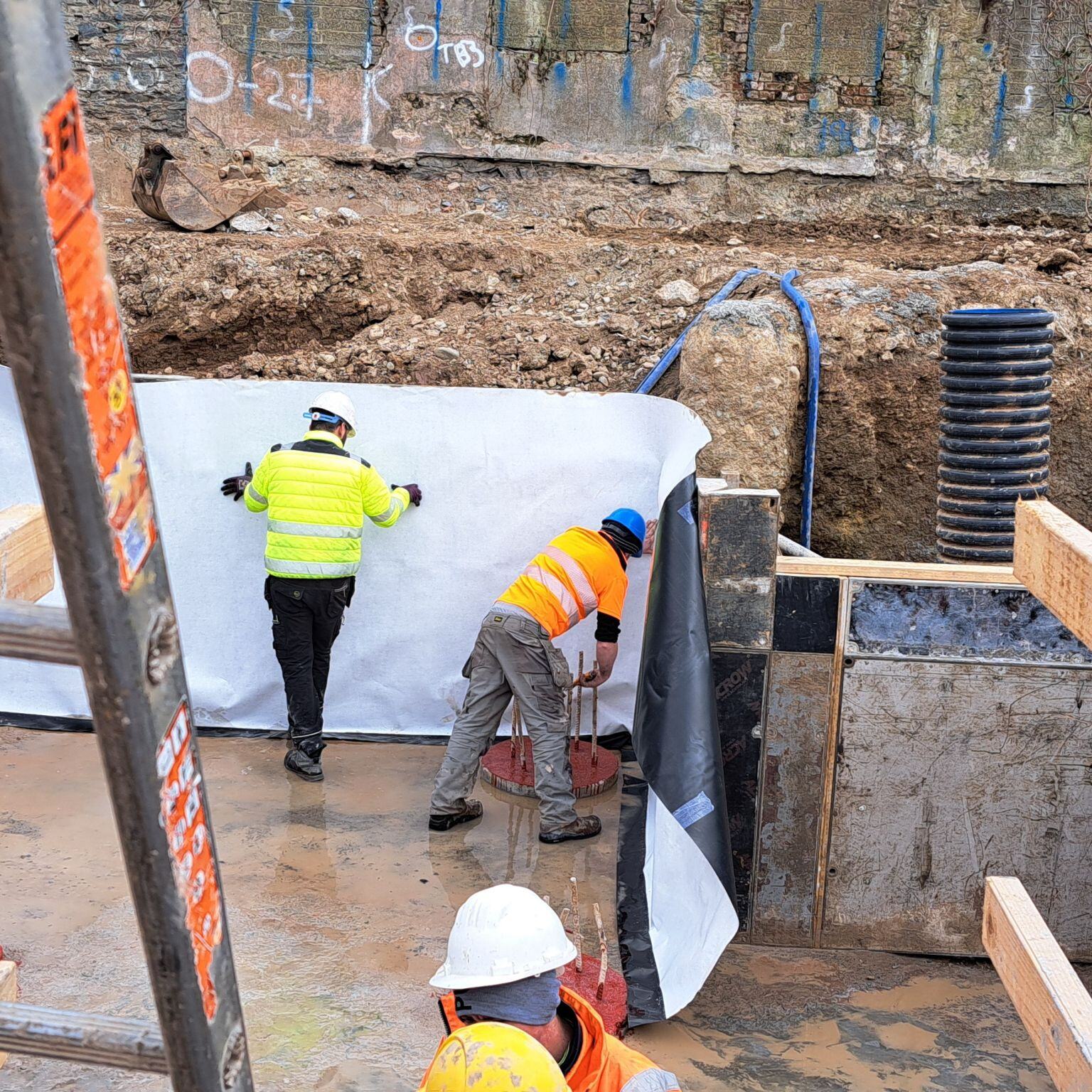
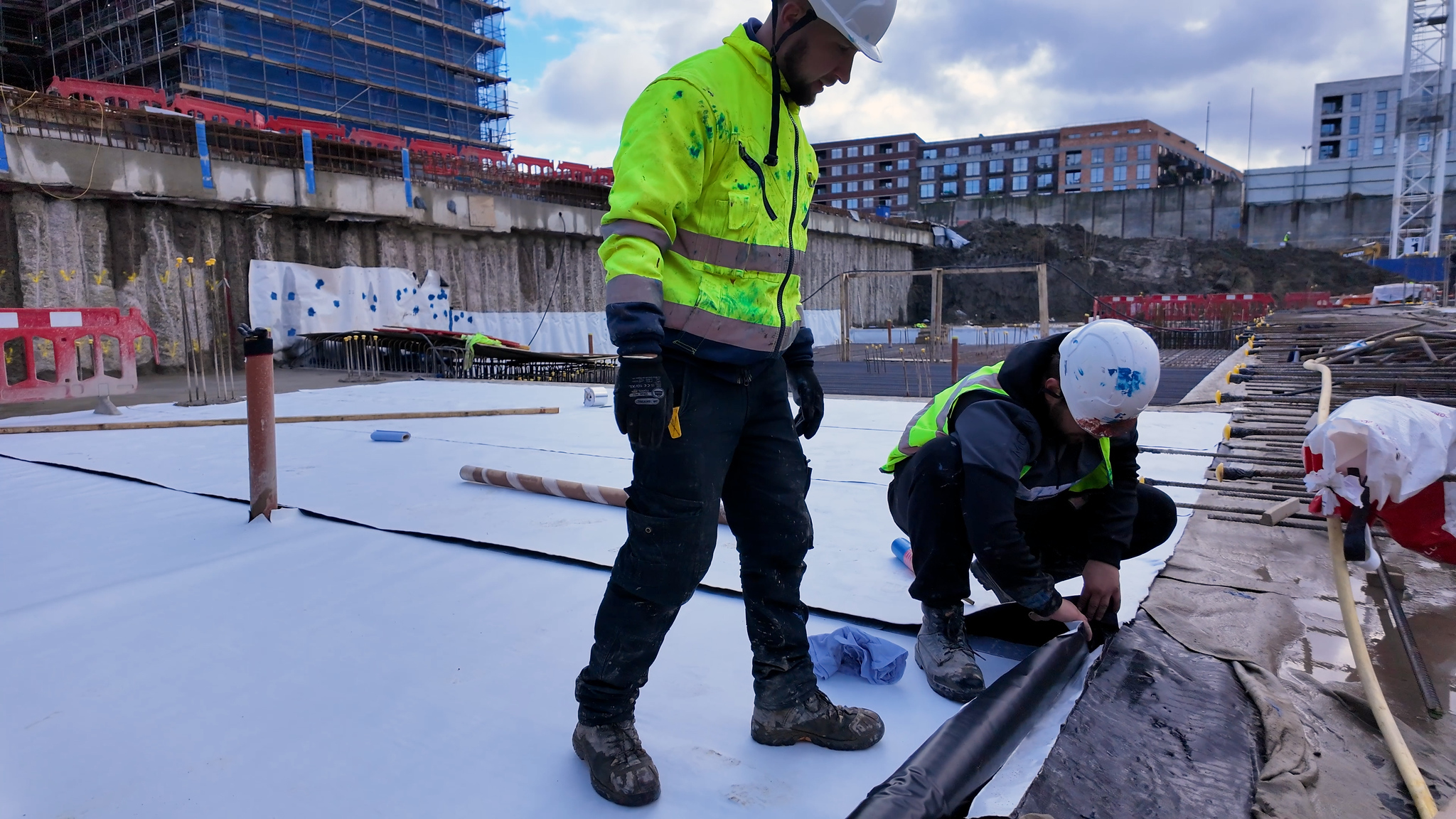
Installation Tips
VOID-TEK panels are designed for easy handling and installation:
Handling: Can be manoeuvred by one or two installers, simplifying the logistics on-site.
Cutting: Easily tailored with a standard utility knife to fit specific dimensions.
Deployment: Quick assembly with minimal risk of breakage or waste.
Mitigate Ground Heave With VOID-TEK From Premcrete
Specifying the correct heave protection board is essential for any construction project involving clay soils. VOID-TEK provides a robust, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution that meets the varying demands of different soil plasticity’s. By following these steps, engineers and construction professionals can ensure that their projects are protected from ground heave without incurring unnecessary costs or delays.
For more information, visit Premcrete’s website or contact their team directly to discuss your specific heave protection needs: sales@premcrete.com

















-1.jpg)